A Secondary Immunodeficiency Disease Is Not the Result of
Nonimmune manifestations are often more easily recognized than those of the immunodeficiency. Immunodeficiency disorders and autoimmune disease are not exactly the same.
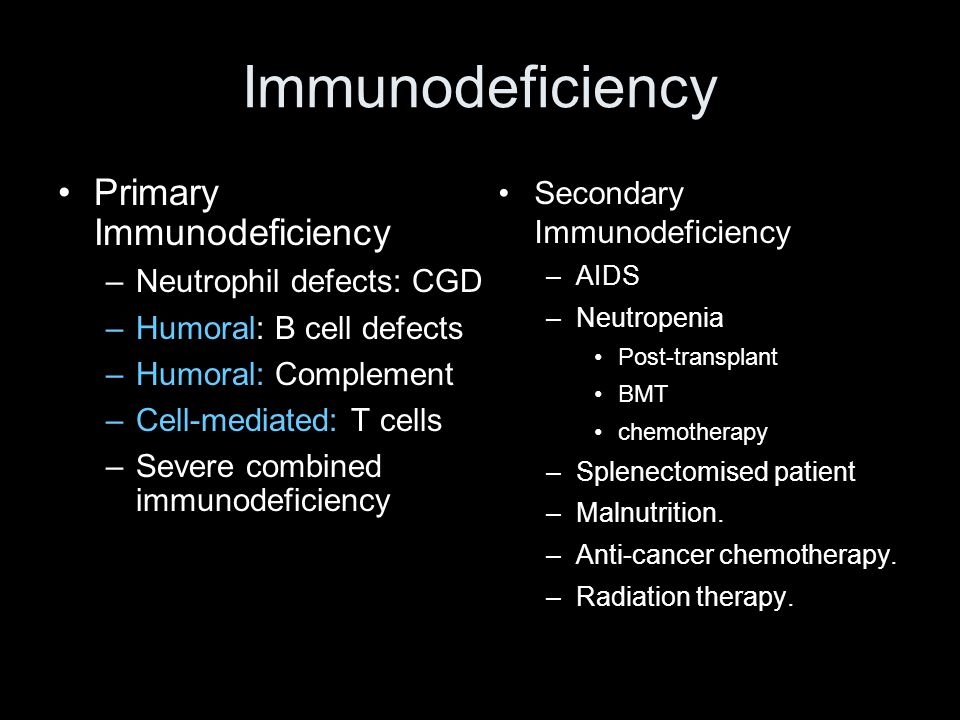
Disorders Of Immunity Immunodeficiency Diseases Ppt Video Online Download
In some cases immune deficiency can also affect the bodys ability to perform its natural function of attacking cells that may become cancerous.
. These immunodeficiencies which can be encountered in routine clinical practice arise from a number of conditions such as treatment with glucocorticoids and immunomodulatory drugs surgery and trauma extreme. X-linked immunodeficiency with hyper IgM syndrome. These disorders generally develop later in life and often result from use of certain drugs or from another disorder such as diabetes or human immunodeficiency virus HIV infection.
Immune deficiencies may be temporary or permanent. These immunodeficiencies can be either primary such as Bruton disease or secondary as the one caused by HIV infection. An immunodeficiency is an.
Secondary or acquired immunodeficiency is one of the major causes of infections in adults. XHM affects only boys and is the result of mutations. These are called secondary immunodeficiencies.
In adult animals immunodeficiencies often result from virus infections malnutrition stress old age or toxins. If youre born with a deficiency from a genetic cause its called primary immunodeficiency. Common infections including influenza and mononucleosis can suppress the immune system.
Secondary immunodeficiency or acquired immunodeficiency is the loss of immune function and results from exposure to various agents. Bone marrow transplant or may remain lifelong patients with complex care needs and the cost-burden on. Secondary causes of immunodeficiency include steroids nutrient deficiency obesity acquired immune deficiency syndrome AIDS or other viral infections.
May be primary due to a defect in the immune mechanism itself or secondary dependent on another disease process specific due to a defect in either the B-lymphocyte or the T-lymphocyte system or both or nonspecific due to a defect in one or another component of the nonspecific immune mechanism. Secondary immunodeficiency disorders are acquired. Systemic disorders such as diabetes mellitus malnutrition hepatitis or HIV infection.
On the other hand a dizzying spiral of. Primary antibody deficiency PAD is the result of intrinsic genetic defects whereas secondary antibody deficiency may arise as a consequence of underlying conditions or medication use. When immune cells are the target of infection severe immune suppression can occur.
On a global level malnutrition HIV and malaria are major causes of secondary immunodeficiency. Examples of secondary immunodeficiency include HIV infection hematopoietic malignancies treatment with radiation and treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. An immune deficiency disease or disorder occurs when the immune system is not working as expected.
These factors put stress on the body and weaken the immune system. If primary immune deficiency diseases are. A secondary immunodeficiency occurs as a result an acquired impairment of function of B cells T cells or both.
And develop as a result of environmental factors. 2 Secondary immunodeficiency Immunomodulatory drugs can severely depress immune functions. Immunodeficiency results from a failure or absence of elements of the immune system including lymphocytes phagocytes and the complement system.
False-positive results from all three laboratories were more 344 CRAWFORD LEVY Table 2 Sensitivity and specificity 95 confidence intervals for three commercial polymerase chain re- action assays PCR1 PCR2 and PCR3 for detection of feline immunodeficiency virus FIV infection in FIV-infected cats unvaccinated uninfected cats and FIV. Severe protein energy malnutrition PEM reduces the efficacy of the immune system. X-linked immunodeficiency with hyper IgM syndrome XHM is a part of the hyper-IgM syndromes that includes a group of disorders characterized by recurrent bacterial infections and low serologic levels of IgG IgA and IgE with relatively elevated levels of IgM.
Cyclophosphamide azathioprine and my cophenolate mofetil act directly on DNA or its synthesis. Secondary immunodeficiency diseases - due to factors that have an adverse impact on the immune system. Extrinsic factors can adversely affect immune responses producing states of secondary immunodeficiency and consequent increased risk of infections.
A condition resulting from a defective immune mechanism. Steroids affect cell traffic induce leucocytopenia and inhibit cytokine synthesis. Immune deficiency or immunodeficiency is the term for any of a number of conditions in immune system loses part or all of its ability to fight infectious disease.
Primary immunodeficiency syndromes are genetically determined immunodeficiencies with immune and nonimmune defects. Secondary immunodeficiencies are the result of disease or other environmental factors weakening the immune system. Ciency diseases are statistically dwarfed by secondary causes of recurrent infection such as malnutrition respiratory allergy chronic cardiovascular pulmonary and renal disease and environmental factors.
The most common secondary immunodeficiency is acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or AIDS which results from infection with the human immunodeficiency virus 1 HIV-1. They are more common than primary immunodeficiency disorders. Deficiency results in reduced production of IFNα IFNß IFNλ TNFα IL-1ß and IL-6 in response to stimulation.
They may occur as a consequence of infection eg. They can also be secondary to disease states including diabetes. 1 Secondary immunodeficiencies result from a variety of factors that can affect a host with an intrinsically normal immune system including infectious agents drugs metabolic diseases and.
Virus-induced secondary immunodeficiencies are the most important of these. Disorders of innate immunity affect phagocytes another component of the immune system and result in severe infections. Examples are ataxia-telangiectasia Ataxia-Telangiectasia Ataxia-telangiectasia results from a DNA repair defect that frequently results in humoral and.
These immunodeficiency disorders affect your immune system partially or. This activity reviews the different immunological disorders their evaluation and management and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in caring for affected individuals. Secondary immunodeficiencies are more common than primary.
Secondary immunodeficiencies are far more common than primary immunodeficiencies which are by definition caused by genetic defects affecting cells of the immune system. Although affecting fewer patients than other classes of immune illness immunodeficiency patients may require expensive definitive therapy eg. Temporary immune deficiency can be caused by a variety of sources that weaken the immune system.
They are not the result of birth but of other circumstances. Secondary immunodeficiencies can be caused by. Secondary immunodeficiency is acquired and is defined by loss or qualitative deficiency in cellular or humoral immune components that occurs as a result of a disease process or its therapy.
Most Common Causes Of Secondary Immunodeficiency In Children Download Table
No comments for "A Secondary Immunodeficiency Disease Is Not the Result of"
Post a Comment